
Can Solar Panels Catch Fire? What Businesses and Property Owners Should Know

Why You Should Clean Your Solar Panels Every Year


The advance of technology and shifting consumer expectations are transforming supply chain logistics.
Those who don’t adapt to these changes will struggle to maintain competitiveness and efficiency, risking failing to keep pace with digital developments and market demands.
The time to prepare for tomorrow is today.
In this article, you’ll discover 5 emerging trends and technologies shaping the future of supply chain logistics.
Stay ahead of the curve with insights on automation, sustainability, and evolving consumer demands.
Advancements in technologies like Generative AI allow logistics professionals to make decisions based on up-to-date insights based on real-time data.
A recent report from Research and Markets shows that AI-equipped supply chains are over 67% more effective than traditional systems, so it’s little wonder that supply chains will continue adopting AI technologies.
Indeed, according to Meticulous Research, the market size for AI in supply chains is projected to reach over $40 billion by 2030, around a 1500% increase from 2022.
This trend means that supply chain professionals should consider AI competency a critical area of focus in the coming years, particularly as more organisations integrate the technology over the next decade.
Meanwhile, machine learning algorithms can analyse large data sets to predict demand, manage inventory, and improve logistics. Other benefits of machine learning tools include:

Improved Warehouse Efficiency: analyse data to optimise warehouse layouts, improve picking and packing processes, and identify bottlenecks.
Supplier Selection and Risk Management: evaluate supplier performance based on quality, delivery time, and pricing.
Cost Reduction: automate repetitive tasks to enhance operations, identify potential issues early, and reduce supply chain costs.
Enhanced Customer Experience: get real-time visibility into order status for improved customer satisfaction.
Predictive Maintenance: analyse equipment data to predict potential failures and minimise downtime.
Sustainability Initiatives: optimise delivery routes and reducing unnecessary transportation for a more sustainable supply chain.
Fraud Detection: identify unusual transaction patterns to detect and prevent fraudulent activity.
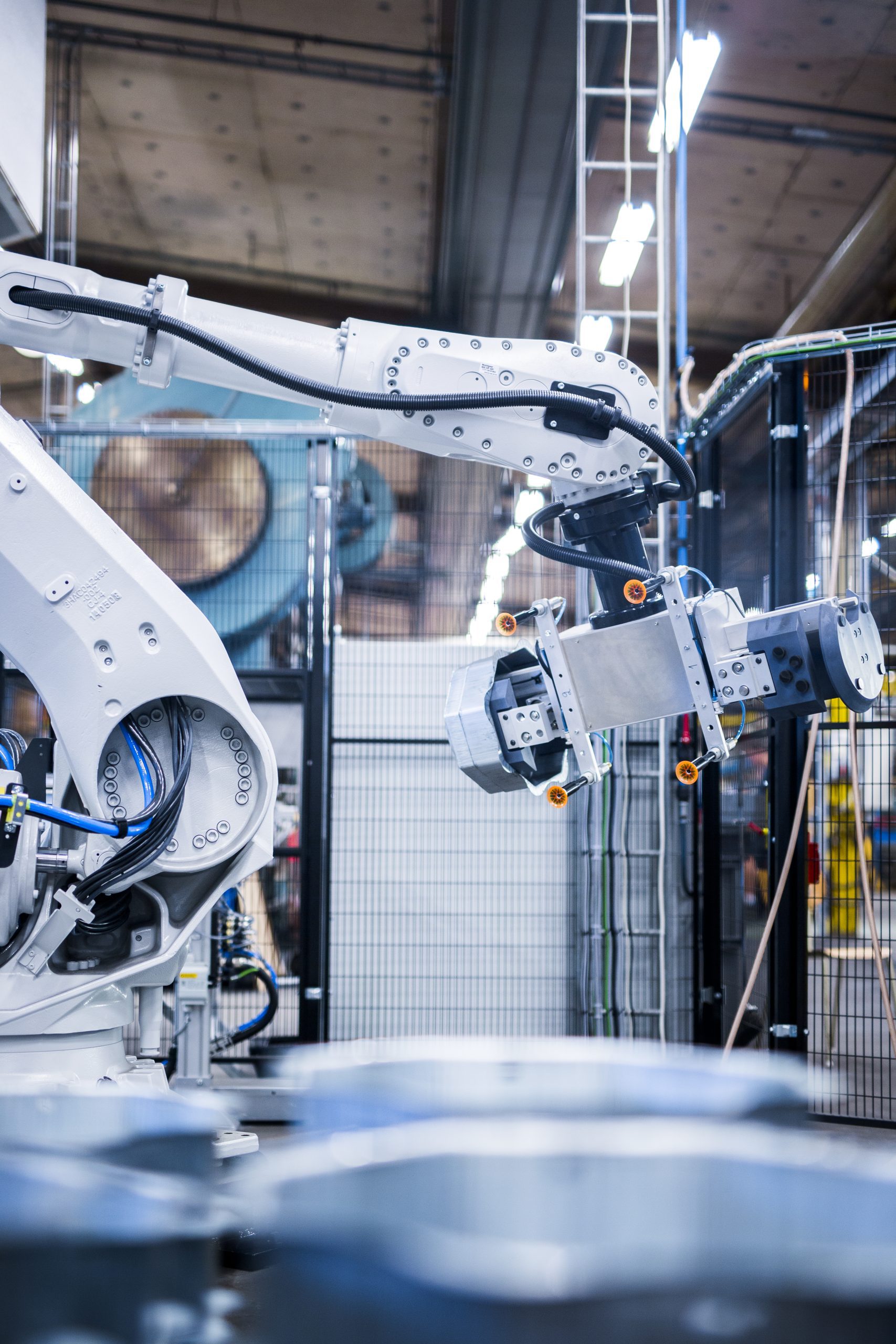
Robotic automation is revolutionising warehouse operations. Using machines with built-in intelligence to lift, move, sort, and pick allows warehouses and distribution centres to increase productivity, accuracy, and safety.
Similarly, modern supply chain professionals use automated systems to manage complicated processes, high-risk tasks and repetitive actions. Automation allows businesses to cut labour costs, streamline operations and boost efficiency.
Recent news from Apptronik shows that the move towards automation and robotics is gaining momentum. The Texas-based, AI-powered humanoid robotics company has raised £350 million in funding to develop Apollo, a human-like robot designed to perform physically demanding warehouse, manufacturing, and other supply chain-oriented tasks.
However Apptronik are not the only company readying themselves for the take-off of this mass market opportunity. Mentee Robotics recently revealed their End-to-End Humanoid, while robotic dogs can already be seen carrying out inspection and surveillance tasks for early adopters Boston Dynamics. Their ‘Spot’ robot dog learns new tricks for inspection tasks.
The future is here.

The Internet of Things (IoT) describes a network of physical objects embedded with sensors and software to exchange information over the Internet.
You’ll already be familiar with several IoT devices useful for supply chain visibility.
For example, RFID chips help identify and track products and containers, and GPS trackers monitor the location of vehicles and shipments. At the same time, temperature and pressure sensors detect potential damage to sensitive goods.
Introducing IoT devices to your supply chain also offers real-time data collection, proactive issue identification, and optimised logistics for improved fleet management and inventory control.
Additionally, supply chain companies using IoT devices see a reduction in potential setbacks such as human error, workforce shortages, missing goods, and adverse weather conditions.

There’s a growing emphasis on eco-friendly supply chain management, from achieving sustainability targets to meeting customer demand for environmentally-conscious products.
Therefore, introducing green initiatives is fundamental to reducing environmental impact and future-proofing your profitability.
One way to reduce logistical carbon emissions is using diesel alternatives, such as Biofuels and Natural Gas. Benefits include reduced pollution and new investment in UK-produced alternative fuels.
However, even though biofuels are renewable and less polluting than fossil fuels, their carbon-producing combustion still carries a negative environmental impact.
Adopting electric vehicles (EVs) in your logistics is a greener fuel option. Using EVs helps improve air quality by reducing exhaust emissions and creating a healthier, cleaner environment.

Circular economy principles assess the potential for introducing practices like designing products with reuse and recycling in mind.
Products that use lightweight, durable, non-polluting materials help reduce waste and protect the environment.
Another example of a circular supply chain principle is renting plastic pallets instead of buying wooden ones. Plastic pallets can be ground down and recycled into new ones, creating a circular supply model that extends the lifespan of pallets.
Discover more about sustainable supply chains here.

The dawn of big data means better supply chain decision-making.
Detailed insights through data analysis enable companies to make informed decisions on the following:
Acting on these insights to identify inefficiencies reduces costs and improves customer satisfaction.
Meanwhile, advances in big data analytics have led to a new approach for visualising and managing complex supply chains – digital twins.
Digital twins are virtual models of physical objects, entities or processes that provide data-rich, mirror representations of their real-world counterparts.

In supply chain management, digital twins provide dynamic, detailed simulation models of existing supply chains for scenario analysis. They offer a comprehensive, real-time view of your entire ecosystem, enabling precise decision-making, better risk mitigation and long-term business continuity.
An adaptable supply chain allows you to swiftly respond to market changes and disruptions.
You can determine your supply chain’s agility by considering the following:
Operational Flexibility: The ability to modify production capacity, volume and mix to accommodate demand or supply changes.
Supply Flexibility: The ability to switch between suppliers, source alternative materials or adjust delivery schedules at a moment’s notice.
Distribution Flexibility: The ability to reconfigure distribution channels, adjust inventory levels and modify transportation modes or routes.
Product Flexibility: The ability to introduce new ranges, modify existing merchandise or customise products according to consumer preferences.

You should also explore ways to identify potential risks and develop contingency plans to mitigate them. Advanced analytics technology helps you proactively manage and navigate supply chain risks.
Want to transform working practices for the better and revolutionise your supply chain?
The modern customer expects a convenient, quick, stress-free buying experience.
One way to meet these demands is by embracing omnichannel order fulfilment.
Omnichannel fulfilment is a strategy that allows businesses to streamline and execute the purchasing process across multiple channels.
From receiving and warehousing to processing, packaging and shipping customers’ orders, this initiative lets logistics providers remain agile, optimise workflows, and efficiently handle orders from multiple channels within a single facility.
Omnichannel fulfilment enables businesses to offer customers modern, user-friendly delivery and collection options, including:

Meanwhile, last-mile delivery innovations like drones and autonomous vehicles are becoming more and more prevalent.
Recently, Waabi, the generative AI pioneer for the physical world, entered a strategic partnership with Volvo Autonomous Solutions to develop and deploy autonomous trucks.
While the roll-out of driverless vehicles has been postponed in the UK, autonomous trucking is expected to usher in a new era of safer, more efficient, and sustainable freight transportation.
Technological advancements, sustainability efforts and evolving customer preferences are reshaping supply chain logistics.
By embracing automation, AI, and green initiatives, your business can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and meet the demands of a dynamic market.
Secure your competitive edge.
Work with Jigsaw Business Group to future-proof your supply chain.
We’ll help you incorporate technologies like real-time monitoring systems to track carbon footprints, optimise resources, and make data-driven decisions that reduce costs and environmental impact.